Solution System
BM027549-UN-09NOV18
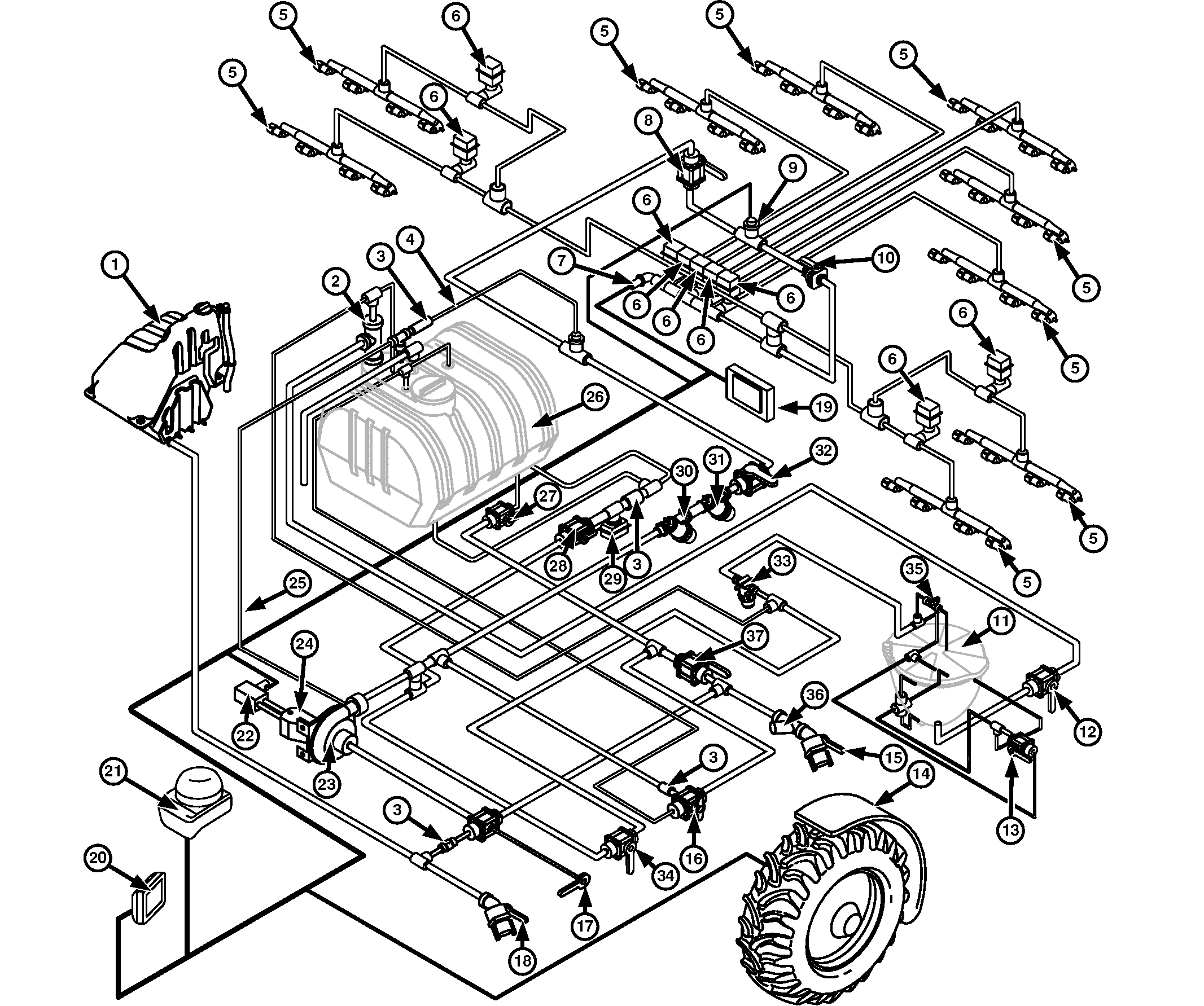
Solution System—M4030 Self-Propelled Sprayer
1 - Rinse Tank
2 - Eductor Venturi
3 - Check Valve
4 - Boom Supply Bleed Line
5 - Spray Nozzles
6 - Spray Boom Section Shutoff Valves
7 - Pressure Transducer
8 - Flowmeter Shutoff Valve
9 - Solution Flowmeter
10 - Orifice Valve
11 - Eductor Hopper
12 - Eductor Hopper Valve
13 - Eductor Rinse Valve
14 - Wheel Speed Sensor (Left-Hand Side Front Wheel)
15 - Solution System Quick Fill™ Valve
16 - Pressure Valve
17 - Suction Valve
18 - Rinse Tank Quick Fill™ Valve
19 - Spray Rate Control Unit (SRC)
20 - CommandCenter™ Display
21 - StarFire™ 6000 Receiver
22 - Proportional Valve
23 - Solution Pump
24 - Hydraulic Motor
25 - Pump Bleed-off Line
26 - Solution Tank
27 - Solution Tank Valve
28 - Agitation Flow Rate Valve
29 - Agitation Solenoid Valve
30 - Solution Strainer (50 Mesh Standard)
31 - Solution Strainer (80 Mesh Standard)
32 - Strainer Shutoff Valve
33 - Eductor Filter
34 - Eductor Flow Rate Valve
35 - Eductor Cover Valve
36 - Fill Strainer (20 Mesh Standard)
37 - Bypass Valve
BM027550-UN-09NOV18
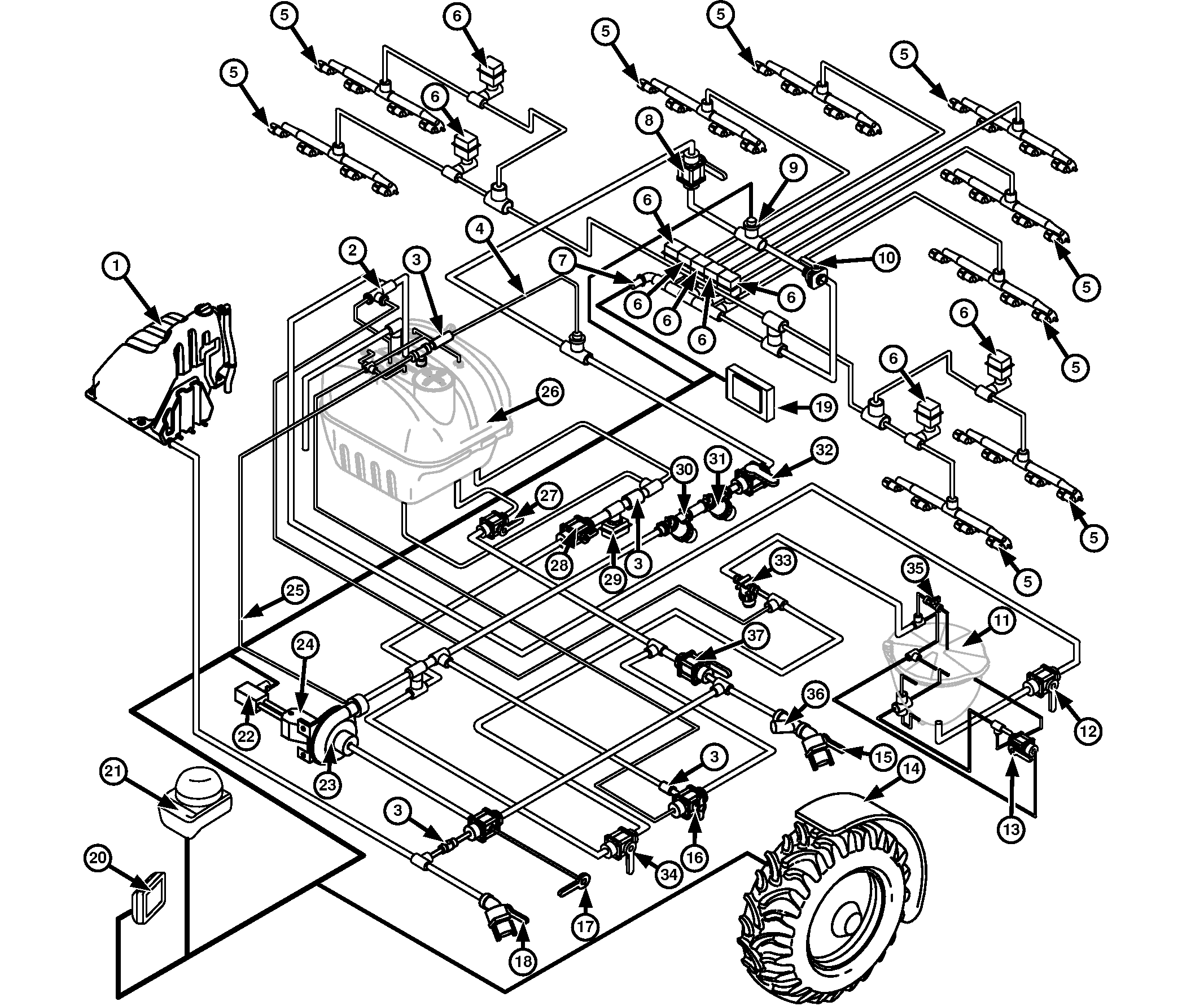
Solution System—M4040 Self-Propelled Sprayer
1 - Rinse Tank
2 - Eductor Venturi
3 - Check Valve
4 - Boom Supply Bleed Line
5 - Spray Nozzles
6 - Spray Boom Section Shutoff Valves
7 - Pressure Transducer
8 - Flowmeter Shutoff Valve
9 - Solution Flowmeter
10 - Orifice Valve
11 - Eductor Hopper
12 - Eductor Hopper Valve
13 - Eductor Rinse Valve
14 - Wheel Speed Sensor (Left-Hand Side Front Wheel)
15 - Solution System Quick Fill™ Valve
16 - Pressure Valve
17 - Suction Valve
18 - Rinse Tank Quick Fill™ Valve
19 - Spray Rate Control Unit (SRC)
20 - CommandCenter™ Display
21 - StarFire™ 6000 Receiver
22 - Proportional Valve
23 - Solution Pump
24 - Hydraulic Motor
25 - Pump Bleed-off Line
26 - Solution Tank
27 - Solution Tank Valve
28 - Agitation Flow Rate Valve
29 - Agitation Solenoid Valve
30 - Solution Strainer (50 Mesh Standard)
31 - Solution Strainer (80 Mesh Standard)
32 - Strainer Shutoff Valve
33 - Eductor Filter
34 - Eductor Flow Rate Valve
35 - Eductor Cover Valve
36 - Fill Strainer (20 Mesh Standard)
37 - Bypass Valve
System Components
The solution spray system consists of the solution tank (26), suction valve (17), solution system Quick Fill™ valve (15), fill strainer (36), pressure valve (16), solution pump (23), solution strainers (30, 31), eductor hopper (11), orifice valve (10), spray boom section shutoff valves (6), and spray nozzles (5) mounted on the boom.
The solution tank (26) is made from polyethylene, and has a capacity of 3028 L (800 gal) for M4030 sprayer and 4000 L (1057 gal) for M4040 sprayer. An access/fill cap is at the top of the tank. At the side of the machine is a clear tube and graduated scale that indicates solution level in liters and gallons. At the bottom of the solution tank (26) is the solution tank valve (27).
The suction valve (17) has two functions:
- Directs solution from the solution tank (26) to the solution pump (23).
- Directs clean water from the rinse tank (1) to the solution pump (23).
The fill strainer (36) located in the solution fill line is constructed of a noncorrosive material that should be cleaned as required. The solution pump (23) is a centrifugal type that is driven by hydraulic motor (24). Engagement and disengagement of the pump is controlled by a switch on the side console. Any air trapped in the pump is allowed to escape through a bleed-off line (25). This helps prevent pump cavitation. A boom supply bleed off-line (4) is also provided on the boom supply line to help remove air from the system.
Solution strainers (30, 31) are located in the boom supply line before the solution flowmeter (9). The solution strainers (30, 31) remove sediment before it reaches flowmeter (9), spray boom section shutoff valves (6) and spray nozzles (5).
The strainer shutoff valve (32) and flowmeter shutoff valve (8) can be closed to aid in cleaning the boom solution strainers (30, 31) and the flowmeter (9).
An orifice valve (10) is on the boom to the left of the flowmeter (9). The orifice valve (10) is used to improve the control of the spray rate control system when smaller nozzles are used. The orifice valve (10) is set in open position for medium to high flow rates and in closed position for a flow rate of 100 L/min (26 gal/min) or less to ensure a correct control of the spray rate measured.
Agitation jets are in two locations on the bottom of the tank. The jet creates a vigorous fan type agitation throughout the tank to keep chemicals, such as wettable powders, in suspension. The agitation flow rate valve (28) is located under the left-hand side of the solution tank and can be adjusted to attain the desired agitation effect. The agitation solenoid valve (29) controlled by a switch on the console can be used to turn the agitation on and off.
Pressure valve (16) does one of three things:
- Directs rinse water of the rinse tank (1) to spray nozzles (5).
- Directs water or solution directly to the tank when filling sprayer with the solution pump (23).
- Stops solution from flowing to the solution tank (26) or tank rinse balls when spraying.
Bypass valve (37) does one of two things:
- Directs solution to the solution pump (23).
- Directs solution to the solution tank (26).
The eductor flow rate valve (34) directs fill water through an eductor venturi (2) at top of the solution tank (26) to create a vacuum to pull the chemical into the water stream. The eductor rinse valve (13) directs water to the eductor hopper (11) rinse and the jug rinse. The eductor hopper valve (12) allows chemical to be drawn from bottom of eductor hopper (11) to top of the solution tank (26).
Check valves (3) are used in the system to prevent solution from flowing in wrong direction.
Spray boom section shutoff valves (6) are motorized ball valves that cycle open or completely closed. The valves are operated by switches on the operator's side console.
The spray nozzles (5), on the center frame and boom, meter, atomize and dispense the solution into specific patterns. Solution flow is metered by the size of the orifice in the nozzle tip. Within limits, solution flow through a nozzle can be increased or decreased by adjusting system pressure.
Most nozzles are designed for optimum performance at specific pressures. However, the range of adjustment is relatively narrow. Line pressures too high or too low effect atomizing the solution and create variations in the spray pattern. The solution atomizes when the liquid is forced through the orifice in the nozzle. The shape of the spray pattern is determined by the shape of the orifice.
The rinse tank (1) can be loaded with clean water for the rinsing solution system.
System Operation
When the pump is activated, solution is drawn from the solution tank (26), through the suction valve (17). The pump (23) pushes the solution through the solution strainers (30, 31) and flowmeter (9) to the spray boom section shutoff valves (6), and to the agitation flow rate valve (28) for agitation.
When the spray boom section shutoff valves (6) are open, the solution flows to the spray nozzles (5), where it is atomized and sprayed.
The flowmeter (9) on the boom sends an electronic signal to the cab control unit (CCU)/spray rate controller (SRC) (19), which compares that signal to the operator-programmed application rate. If there is a difference in the signal from the flowmeter (9) and the programmed rate, the compensators in the proportional valve (22) open or close as needed until the system is stabilized.
When the compensator opens, more hydraulic oil is sent to the hydraulic motor (24), causing the solution pump (23) to increase its flow. When the compensator closes, less hydraulic oil is sent to the hydraulic motor (24), causing the solution pump (23) to decrease its flow.
The Spray Rate Controller (SRC) (19) provides the ability to maintain application within a range of application rates while changing speeds. Application rate consistency depends on a number of things such as nozzle tip size, application rate, and rate of speed change. The Spray Rate Control Unit (SRC) (19) provides quick response, but some differences in application rates can be observed if the operator makes rapid speed changes or operates at the extremes of the solution pressure range.
Principle part of the Spray Rate Controller (SRC) (19) system are a wheel speed sensor (14) on the left-hand side front wheel motor, the Spray Rate Control Unit (SRC) (19), a variable speed solution pump (23), flowmeter (9), and a solution pressure transducer (7). The speed sensor (14) and flowmeter (9) provide speed and flow rate information to the spray rate controller. The spray rate control unit provides target (programmed by the operator) application rates by analyzing speed and flow data, and then making appropriate adjustments to the variable solution pump (23).
The Spray Rate Control Unit (SRC) (19) is part of the Spray Boom Height Control Unit (BHC), located on the rear of the machine below the spray boom lift hardware. The Spray Rate Control Unit (SRC) (19) has an internal warning system that alerts the operator if the actual flow rate varies from the programmed flow rate by 20% of actual or more for 10 seconds. The Spray Rate Control Unit (SRC) (19) system is a volume-regulating system, so pressures displayed on the CommandCenter™ display (20) may vary at a given ground speed.
The solution pressure required for a given application rate is determined by speed and nozzle tip size. Before attempting to use the SRC, refer to a nozzle tip calculator or nozzle tip selection charts, and make sure that the spray boom is equipped with spray tip nozzles that will provide desired application rates at desired pressures and speeds. Ground speed variation is limited by the operating pressure range of the nozzle tips.
The master on-off button located on the multi-function lever is an integral part of the SRC system. When “off” is pushed, electrical power closes the spray boom section shutoff valves (6) and the variable solution pump (23) slows to maintain spray-off pressure (as set by the operator).
Solution may continue to spray from the boom for a short period of time after master “off” is pushed. This is due to pressure remaining in the line. The time interval that spray continues flowing depends upon pressure in the spray line, boom hose lengths and routings, nozzle tip size, and use of the nozzle check valves. To compensate for the boom shutoff lag time, master off should be pressed prior to reaching the headland.
Once master “on” has been pressed, if the machine is moving slowly or is not moving, the variable solution pump (23) maintains the minimum solution pressure as set by the operator. This may result in an application rate that is higher than the target rate (programmed by the operator). Likewise, if the machine is moving too fast, the variable solution pump (23) maintains the maximum solution pressure. This may result in an application rate that is lower than the target rate.
|
Quick Fill is a trademark of Deere & Company CommandCenter is a trademark of Deere & Company StarFire is a trademark of Deere & Company |
TS95756,00007D8-19-20181210 |