Loading the Cargo Box
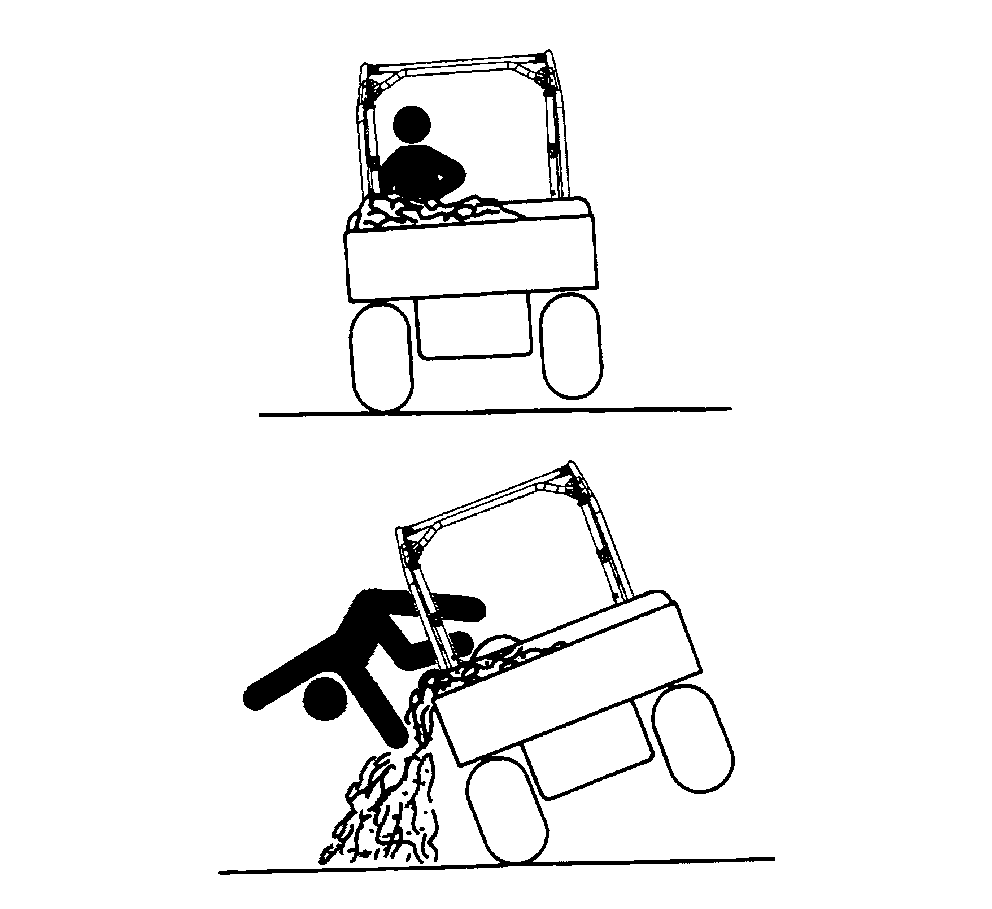
 CAUTION: The utility vehicle may become unstable if the cargo
box is loaded incorrectly. Avoid loose and shifting loads or uneven
loading of material.
CAUTION: The utility vehicle may become unstable if the cargo
box is loaded incorrectly. Avoid loose and shifting loads or uneven
loading of material.
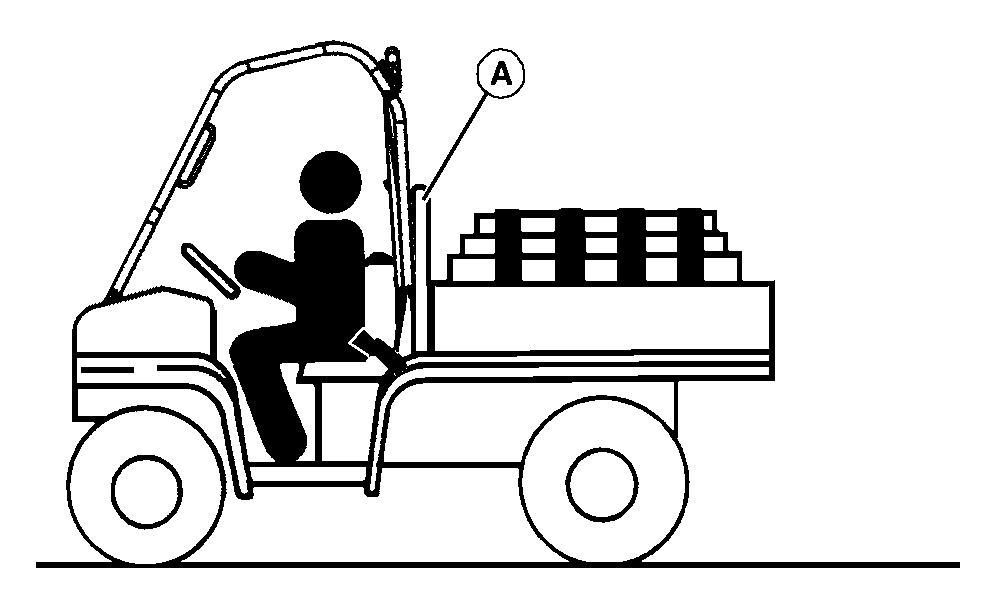
- Do not load above height of load guard.
- Securely anchor all loads in cargo box.
- Do not load beyond maximum capacity.
MXAL44182-UN-10APR13
See capacities in SPECIFICATIONS.
Reduce load by half when operating over rough, hilly, or steep terrain. Do not overload vehicle. Limit loads to those that can be safely controlled.
Reduce speed and exercise extreme caution when operating over rough, hilly, or steep terrain.
Securely anchor and evenly distribute loads in cargo box, when loading objects into vehicle. Shifting loads will affect stability.
Do not load above load guard (A).
MXAL44183-UN-10APR13
Avoid concentrated loads at rear or side of cargo box to prevent vehicle from tipping over. Be sure load is evenly distributed.
Because there is a big difference in weight between dry and wet sand, the only way of getting true weight of the load you are carrying is by using a scale.
Printed weight is normally on bagged and other material.
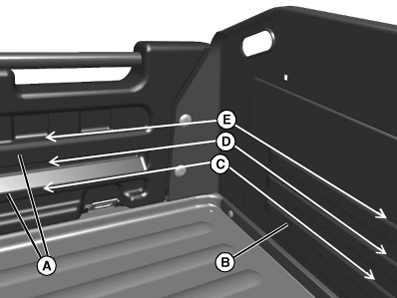
Box Volume Capacity
MXAL44184-UN-10APR13
Use rub rails (A) in left and right side panels, and form beads (B) in cargo box front panel to determine cargo box volume.
- 10.1 cm (4 in.) load height (C) = 150 L (5.3 cu ft).
- 15.2 cm (6 in.) load height (D) = 226 L (8 cu ft).
- 20.3 cm (8 in.) load height (E) = 303 L (10.7 cu ft).
NOTE: Use table below to determine height of common cargo box materials.
Do not exceed Gross Vehicle Weight (GVW).
|
Material |
Weight (lbs/cubic foot) |
Capacity Height |
|---|---|---|
|
Asphalt |
45 |
12 |
|
Brick |
120 |
6 |
|
Cement (Dry) |
94 |
8 |
|
Sand (Dry) |
100 |
7 |
|
Sand (Damp) |
120 |
6 |
|
Sandstone (Broken) |
94 |
8 |
|
Concrete (Set/Mix) |
135 |
5 |
|
Soil (Dry/Loose) |
78 |
9 |
|
Soil (Wet/Packed) |
100 |
7 |
|
Clay (Dry/Lump) |
67 |
11 |
|
Clay (Wet/Lump) |
100 |
7 |
|
Fertilizer |
60 |
12 |
|
Gravel (1/4 - 2 in.) |
105 |
7 |
|
Turf/Sod |
35 |
12 |
|
MX00654,00000D0-19-20130826 |