Determining Vehicle Load Capacity
Find weights and capacities for your machine model in SPECIFICATIONS.
 CAUTION: Avoid injury! Overloading the vehicle or trailer causes
loss of control and causes serious injury or death.
CAUTION: Avoid injury! Overloading the vehicle or trailer causes
loss of control and causes serious injury or death.
- Do not allow the Gross Vehicle Weight (GVW) to exceed the Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) of the vehicle.
- Remove excess weight before operating vehicle.
MXAL44181-UN-10APR13
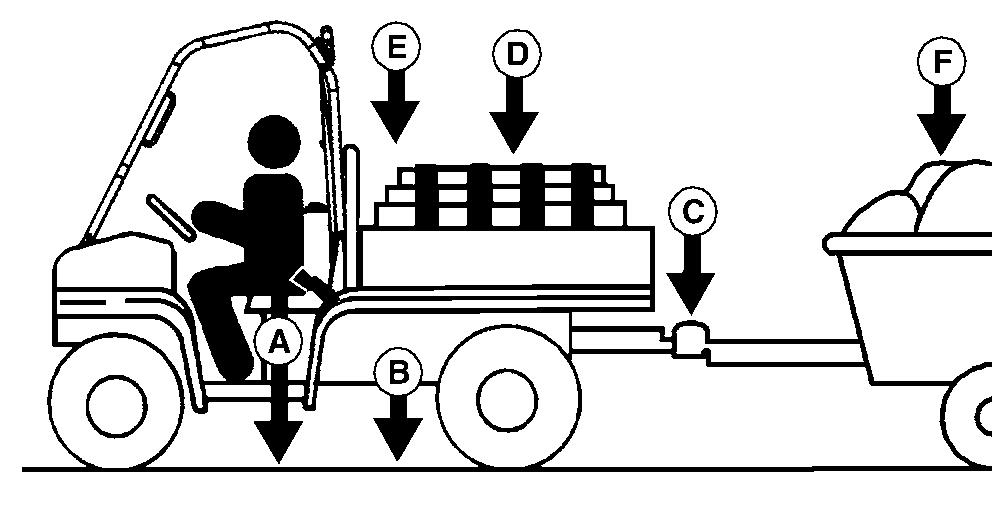
Factors in Determining Vehicle Load Capacity
NOTE: Optional equipment or attachments that are not standard equipment, must be included when determining gross vehicle weight, and cargo box capacity is reduced.
-
Gross Vehicle Weight (GVW) is the
combination of the empty vehicle weight, payload, trailer tongue weight,
and the weight of any other kits or attachments on the vehicle.
GVW = A+B+C+D+E
- Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) is the maximum permissible vehicle weight.
- Payload is the weight of all occupants plus the cargo box load.
- (A) Occupant load is the combined weight of all occupants (operator and one passenger).
- (B) Empty vehicle weight is the weight of the vehicle (full fluids) without occupants or load or attachments.
- (C) Trailer tongue weight is the weight measured if the tongue of a loaded trailer was placed on a scale. The tongue weight must be approximately 10% of the total of the trailer weight and the weight of its load.
- (D) Cargo box load is the weight of the cargo in the cargo box. The weight is less depending on the weight of the occupants, attachments, and the trailer tongue weight.
- (E) Attachment and Option weight is the combined weight of all attachments and options that were not standard equipment. See your John Deere dealer for help with this information.
- Vehicle Load capacity is the remaining amount of weight that the vehicle can haul in the cargo box and/or the additional weight from the operator, passenger, trailer tongue, and attachments.
-
Determine maximum vehicle load capacity:
- Calculate GVW = A+B+C+D+E
- Subtract the Gross Vehicle Weight (GVW) from the Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR).
-
The weight difference between the two numbers is the vehicle
load capacity.
Vehicle Load Capacity=GVWR-GVW
- The Gross Vehicle Weight must be less than or equal to the Gross Vehicle Weight Rating. If GVW exceeds GVWR, remove excess weight from vehicle before operating.
Example:
The following example is for an XUV 825i with a 68 kg (150 lb.) cargo load, a 91 kg (200 lb.) operator, 100 kg (220 lb.) of attachments and options (such as a heavy duty brush guard, OPS poly roof, cargo box power lift kit); towing a trailer with 23 kg (50 lb.) of tongue weight.
|
Key |
Description |
|---|---|
|
(A) Operator Weight: |
91 kg (200 lb.) |
|
(B) XUV 825i: |
763 kg (1682 lb.) |
|
(C) Trailer Tongue Weight: |
23 kg (50 lb.) |
|
(D) Cargo Load: |
68 kg (150 lb.) |
|
(E) Attachments and/or Options: |
100 kg (220 lb.) |
GVW = 1044 kg (2302 lb.) [91 kg (200 lb.) + 763 kg (1682 lb.) + 23 kg (50 lb.) + 68 kg (150 lb.) + 100 kg (220 lb.)]
Vehicle Load Capacity = GVWR 1406 kg (3100 lb.) less GVW 1044 kg (2302 lb.)
Vehicle Load Capacity = 362 kg (798 lb.)
The remaining vehicle load capacity of 362 kg (798 lb.) can be used to haul additional passenger, cargo, trailer tongue, and attachment weight.
|
OUMX068,0000999-19-20140924 |