INFO tab
PC13046-UN-10NOV10
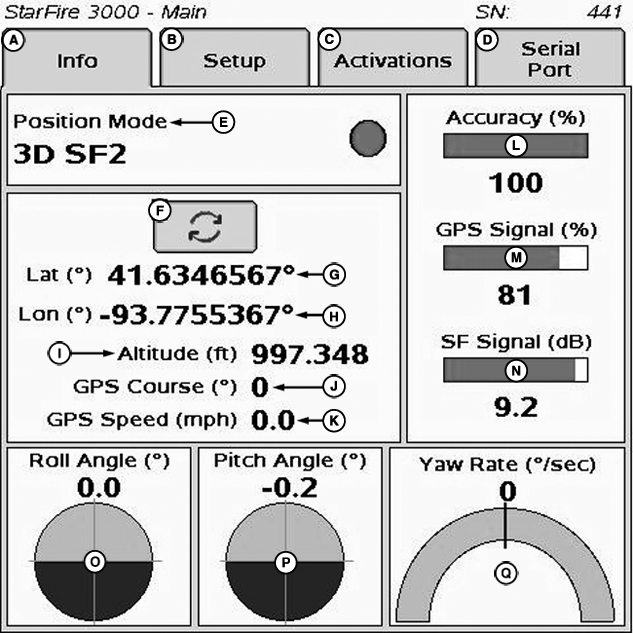
StarFire 3000 - Main—Info Tab
A - Info tab
B - Setup tab
C - Activations tab
D - Serial Port tab
E - Position Mode
F - Degrees/Minutes/Seconds to Decimal Toggle
G - Latitude
H - Longitude
I - Altitude
J - GPS Course
K - GPS Speed
L - Accuracy
M - GPS Signal
N - SF Signal
O - Roll Angle
P - Pitch Angle
Q - Yaw Rate
The INFO tab shows information and status of incoming GPS and SF correction signals. No information on this screen can be changed. It is for viewing only:
- Position Mode: Indicates whether receiver is calculating a 3-D position, 2-D position, or no position (No Navigation). It also shows status of SF signal: SF1 (StarFire 1 differential), SF2 (StarFire 2 differential), RTK (Real Time Kinematic differential), and RTK-X (Real Time Kinematic—Extended differential).
- Lat (G): Displays vehicle location latitude coordinates with respect to Equator (north or south).
- Lon (H): Displays vehicle location longitude coordinates with respect to Prime Meridian (east or west).
NOTE: TOGGLE button allows operator to change the way latitude and longitude are displayed from degrees/minutes/seconds to decimal degrees.
- Altitude: displays height of receiver, measured from top of dome, in meters (feet) above sea level.
- GPS course: Displays direction of travel, in degrees relative to true north (zero degrees) as measured by receiver. Angle is measured in clockwise direction.
NOTE: Course and speed normally show small speeds and various courses even when machine is not moving.
- GPS speed: displays ground speed of machine in miles per hour (kilometer per hour) as measured by receiver.
- GPS Accuracy Indicator (GPS AI): GPS AI gives indication of GPS position accuracy achieved by receiver, and is displayed as a percentage (0-100%)
When receiver is initially powered, GPS AI displays 0%. As receiver acquires satellites and calculates a position, GPS AI increases as accuracy improves. Acceptable guidance performance for Parallel Tracking and AutoTrac is achieved when GPS AI displays 80% or greater. Satellite acquisition may take up to 20 minutes. Many factors affect GPS accuracy. If 80% accuracy or greater is not achieved within 25 minutes, consider the following possibilities:
- Unobstructed view of sky – trees, buildings, or other structures block receiver signals from available satellites.
- L1/L2 signal to noise ratio (SNR) – radio interference from 2-way radios or other sources causes low SNR (check satellite button – Graph).
- Satellite position in sky – poor GPS satellite geometry can reduce accuracy (check satellite button – SkyPlot).
- Number of satellites in solution – total number of satellites receiver uses to calculate a position (check satellite button– SkyPlot).
- GPS Signal Quality: Displays quality of signals being received from constellation of GPS satellites.
- SF Signal Quality: Displays quality of SF correction signal received by receiver.
-
TCM (Terrain Compensation Module):
- Roll Angle: Is both a graphical and numerical representation of amount of roll TCM is measuring, relative to calibrated zero degree reference. Positive roll angle—vehicle is rolled to the right (depicts what horizon would look like from cab).
- Yaw Rate: Graphic representation and a numeric figure for amount of rotation TCM is measuring. Positive yaw rate—vehicle is turning right.
- Pitch Angle: Positive pitch angle occurs when vehicle cab is tilted back and negative pitch angle occurs when vehicle cab is tilted forward.
|
DK01672,0000195-19-20110926 |