Compact Utility Tractor with Gear Transmission
Introduction
Safety Signs
Controls
Operating
Replacement Parts
Service Machine Safely
Service Intervals
Service Engine
Service Transmission
Service Electrical
Service Miscellaneous
Lubricating Tractor Grease Fittings
Lubricating Standard Tractor Grease Fittings
Lubricating Optional 4WD Tractor Grease Fittings
Avoid Damage to Plastic and Painted Surfaces
Front Tire Inflation Pressures
Troubleshooting
Storing Machine
Assembly
Specifications
Warranty
John Deere Service Literature
John Deere Quality Statement

Service Miscellaneous
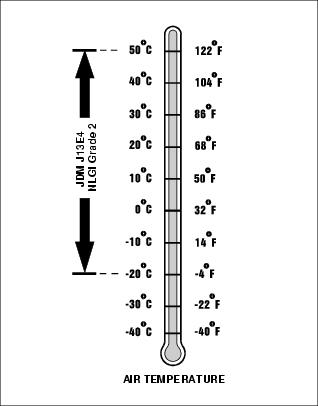
Grease
Use the following gear grease based on the air temperature range. Operating outside of the recommended grease air temperature range may cause premature failure.
IMPORTANT: Avoid damage! ONLY use a quality grease in this application. DO NOT mix any other greases in this application. DO NOT use any BIO-GREASE in this application. |
The following John Deere gear grease is PREFERRED:
Other greases may be used if above John Deere greases are not available, provided they meet the following compatibility specifications only:
· John Deere Standard JDM J13E4, NLGI Grade 2
Lubricating Tractor Grease Fittings
NOTE: The drawings of the service lubrication areas are from the bottom of the tractor.
Lubricating Standard Tractor Grease Fittings
Lubricate all fittings with John Deere Multipurpose Grease. (See Fuels and Lubricants Section.)
Lubricating Optional 4WD Tractor Grease Fittings
Lubricate all fittings with John Deere Multipurpose Grease. (See Fuels and Lubricants Section.)
Diesel Fuel Specifications
In general, diesel fuels are blended to satisfy the low air temperature requirements of the geographical area in which they are sold.
Diesel fuel is usually specified to ASTM D975 and sold as either Grade 1 for cold air temperatures or Grade 2 for warm air temperatures.
If diesel fuels being supplied in your area DO NOT meet any of the above specifications, use diesel fuels with the following equivalent properties:
· Cetane Number 40 (minimum). A cetane number greater than 50 is preferred, especially for air temperatures below -20°C (-4°F) or elevations above 1500 m (5000 ft).
· Cold Filter Plugging Point (CFPP). The temperature at which diesel fuel begins to cloud or jell. Use diesel fuels with a CFPP which is at least 5°C (9°F) below the expected low air temperature.
· Sulfur Content of 0.05% (maximum). Diesel fuels for highway use in the United States now require sulfur content to be less than 0.05%. If diesel fuel being used has a sulfur content greater than 0.5%, reduce the service interval for engine oil and filter by 50%.
Bio-Diesel Fuels with bio-degradable properties that meet specification DIN 51606 or equivalent may be used.
Consult your local diesel fuel distributor for properties of the diesel fuel available in your area.
Lubricity
Diesel fuel must have adequate lubricity to ensure proper operation and durability of fuel injection system components. Fuel lubricity should pass a minimum of 3300 gram load level as measured by the BOCLE scuffing test.
Avoid Damage to Plastic and Painted Surfaces
· Insect repellent spray may damage plastic and painted surfaces. Do not spray insect repellent near machine.
· Be careful not to spill fuel on machine. Fuel may damage surface. Wipe up spilled fuel immediately.
· Do not wipe dry surface with dry cloth. Plastic and painted surfaces may scratch.
Fuel Storage
It is recommended that diesel fuel be stored ONLY in a clean, approved POLYETHYLENE PLASTIC container WITHOUT any metal screen or filter. This will help prevent any accidental sparks from occurring. Store fuel in an area that is well ventilated to prevent possible igniting of fumes by an open flame or spark. This includes any appliance with a pilot light.
Keep fuel in a safe, protected area and in a clean, properly marked ("DIESEL FUEL") container. DO NOT use de-icers to attempt to remove water from fuel. DO NOT use de-icers to attempt to remove water from fuel. DO NOT depend on fuel filters to remove water from fuel. It is recommended that a water separator be installed in the storage tank outlet. BE SURE to properly discard unstable or contaminated diesel fuel and/or their containers when necessary.
Filling the Fuel Tank
IMPORTANT: Avoid damage! Avoid spilling fuel. Fuel can damage plastic and painted surfaces. Fuel tank capacity is approximately 24 L (6.3 gal). |
2. Fill fuel tank at end of each day's operation to prevent condensation in fuel tank as moist air cools.
3. Fill fuel tank when fuel gauge shows 1/4 or less fuel in tank.
Changing Rear Tread
To provide best stability, operate tractor with rear wheels mounted in the wide tread position whenever possible.
IMPORTANT: Avoid damage! Always make sure tires rotate in proper direction. Arrows on sidewall should point in direction of forward rotation. |
· Move wheel from one side of tractor to the other (A) to maintain proper direction of tire rotation.
· Tighten tractor front wheel lug bolts to 133 N·m (98 lb-ft). Tighten tractor rear wheel lug bolts to 186 N·m (137 lb-ft). Check and retighten bolts as instructed in service section.
· Tread width dimensions are shown in the following charts. Tread width is measured between centers of tires
Tread Width Specifications
Service Tires Safely
Explosive separation of a tire and rim parts can cause serious injury or death.
DO NOT attempt to mount a tire unless you have the proper equipment and experience to perform the job.
Always maintain the correct tire pressure. Do not inflate the tire above the recommended pressure. Never weld or heat a wheel and tire assembly. The heat can cause an increase in air pressure resulting in a tire explosion. Welding can structurally weaken or deform the wheel.
When inflating tires, use a clip-on chuck and an extension hose long enough to allow you to stand to one side and NOT in front of or over the tire assembly. Use a safety cage if available.
Check wheels for low pressure, cuts, bubbles, damaged rims or mission lug bolts and nuts.
Checking Wheel Bolt Torque
Anytime hardware is loosened, it MUST be retightened to specified torque:
1. Tighten FRONT wheel bolts to 133 N·m (98 lb-ft).
2. Tighten REAR wheel bolts to 186 N·m (137 lb-ft).
NOTE: Follow checking procedure when a new tractor is first used, or when wheels have been removed.
· After driving tractor about 100 m (109 yds.), and before placing it under load, retighten hardware to specified torque.
· Check hardware after operating tractor for 3 hours and again after 10 hours.
· Check all hardware frequently and keep it tight.
Checking Tire Pressure
2. Check tire pressure with an accurate gauge. See next page for recommended tire pressures.
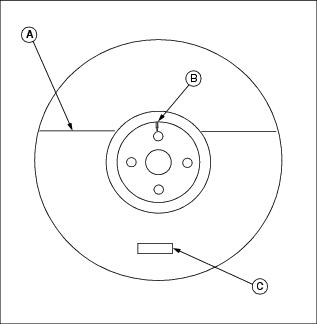
Front Tire Inflation Pressures
Rear Tire Inflation Pressures
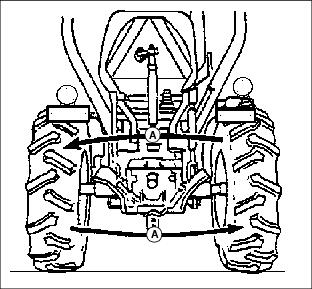
Adjusting Toe-In
1. Park tractor on level surface.
2. Turn steering wheel so front wheels are in the straight-ahead position.
3. Lower attachment to ground. Lock park brake. Stop engine. Remove key.
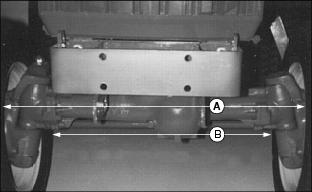
4. Measure distance between tire beads (A) at front of tire, hub height.
5. Measure distance between tire beads (B) at rear of tire, hub height.
6. Front distance should be 3-9 mm (1/8-3/8 in.) less than rear distance. If not, adjust tie rod length.
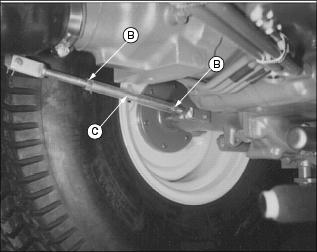
7. Loosen tie rod nut (C) on both tie rod ends.
8. Turn tie rod until toe-in is to correct specification.
Adjusting Brakes
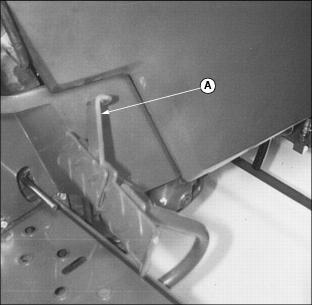
· With brake pedals not locked together (A) as shown, depress both pedals to where they firmly engage brakes. The two pedals should be at the same height when brakes are engaged. If height is not equal, adjust free travel.
2. Measure distance each pedal travels at top of stroke before engaging brakes. Adjust free travel if it is more than 35 mm (1-3/8 in.).
NOTE: Tighten Lock nuts. Adjust other side in same manner.
3. Loosen linkage rod lock nuts (B). Rotate turnbuckle (C) to shorten rod. Adjust free travel to 25 mm (1 in.). KEEP BOTH PEDALS ADJUSTED EVENLY.
4. When linkage has no adjustment remaining, see your John Deere dealer for repair service.
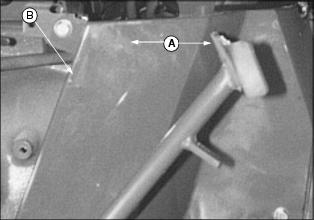
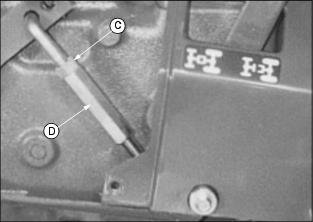
Adjusting Clutch
1. Measure free travel at top of pedal stroke (A). If free travel is 15 mm (5/8 in.) or less, adjust linkage to obtain 35 mm (1-3/8 in.) travel.
2. Remove shield (B) to adjust clutch.
3. To adjust linkage, loosen lock nut (C) and rotate turnbuckle (D). Recheck free travel and retighten lock nut.